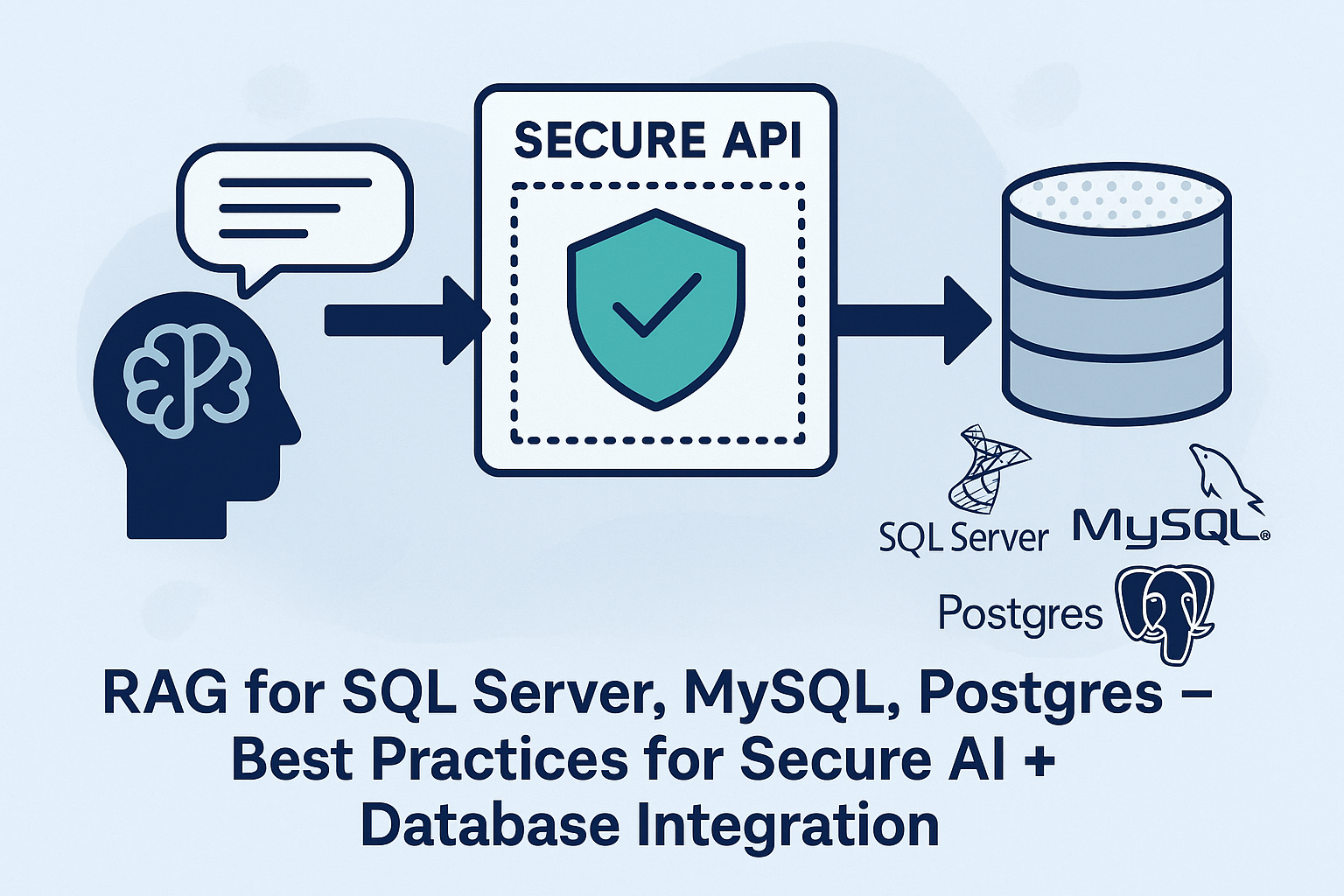
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) lets LLMs deliver current, context-rich answers by fetching live data—customer records, knowledge articles, metrics—from SQL Server, MySQL, and PostgreSQL. Reports suggest RAG can boost answer accuracy dramatically (in some cases up to 90%), making it compelling for BI, support, and operations. The challenge: enabling on-the-fly retrieval without opening security, compliance, or scalability risks.
Executive takeaway: Don’t let LLMs write SQL. Put a secure API gateway between AI and your databases. Enforce zero-trust, parameterization, RBAC, masking, and full-fidelity audit logs.
Why Direct DB Access from an LLM Is Risky
- Prompt ➜ SQL injection: Malicious or “poisoned” prompts can coerce unsafe queries.
- Credential exposure: Embedding DB creds in tools or prompts risks leaks.
- Business rule blindness: Freeform SQL can bypass policy filters and PII controls.
- Performance regressions: Inefficient AI-written queries can crush production.
A Secure Pattern for RAG: API Gateway Mediation
Instead of direct SQL, expose pre-approved, parameterized REST endpoints. Your RAG pipeline (LangChain, LlamaIndex, custom agents) calls these endpoints to retrieve context. The LLM never sees SQL or credentials—only structured JSON.
Gateway Requirements
- RBAC with least privilege (separate read-only roles).
- API keys/OAuth2, short-lived tokens, rotation.
- Parameterization & input validation at every endpoint.
- Field/row-level policies, masking, residency controls.
- Rate limits, concurrency caps, timeouts, pagination.
- Comprehensive logs: who/what/when/where/result.
DreamFactory MCP Fit
- Auto-generates REST APIs for SQL Server, MySQL, Postgres.
- Swagger/OpenAPI & strict input schemas out of the box.
- RBAC, keys/OAuth, parameterization, validation built-in.
- Server-side scripting for masking and business rules.
- Zero-credential exposure to the LLM (gateway holds secrets).
- Centralized auditing & SIEM-friendly logs.
Reference Architecture: Secure RAG with SQL
- Retriever/Agent detects a need for data (e.g., “get order history for customer 123”).
- Policy check ensures role, scope, and quota allow the call.
- DreamFactory MCP invokes a vetted endpoint like
GET /api/orders?customer_id=123&limit=50with:- Parameterization and type validation
- Field allowlist and result-size limits
- Row-level filters by tenant/region
- Backend (SQL Server/MySQL/Postgres) executes via a restricted service account.
- Response returns JSON to the retriever; masking rules applied server-side.
- Observability exports logs/metrics/traces to your SIEM/APM.
Endpoint Patterns (Vendor-Agnostic)
|
Use case |
Example Endpoint |
Notes |
|---|---|---|
|
Customer lookup |
|
Field allowlist; email regex; limit=1 |
|
Order history |
|
Time-bounded; pagination; read-only role |
|
Knowledge articles |
|
Sanitized search; result-size caps |
|
Ticket summaries |
|
Row-level policy by team/tenant |
Secure-by-Default Controls You Should Enforce
- Least-privilege roles:
rag-readerwith read-only to specific views. - Views instead of base tables: Encode business filters & masking into SQL views.
- Strict schemas: Validate types, enums, ranges; reject unknown params.
- Response shaping: Remove secrets/PII server-side; cap rows/columns.
- Egress guardrails: Max payload size, result truncation with reasons.
- Data residency: Route queries to in-region replicas; tag responses with region.
Concrete Examples (SQL Server, MySQL, Postgres)
1) Orders by Customer (parameterized, paginated)
# Example cURL (gateway token, not DB creds)
curl -H "Authorization: Bearer <API_TOKEN>" \
"https://api.example.com/api/orders?customer_id=123&limit=50&from=2025-01-01&to=2025-12-31"2) Field Masking (server-side script)
// Before returning JSON, mask PII-like fields
{
"customer_id": 123,
"email": "j***@example.com",
"last4_cc": "1234",
"orders": [ ... ]
}3) Tool/Function Declarations for RAG Orchestrators
{
"name": "get_orders",
"description": "Fetch recent orders for a customer.",
"parameters": {
"type":"object",
"properties":{
"customer_id":{"type":"integer"},
"from":{"type":"string","format":"date"},
"to":{"type":"string","format":"date"},
"limit":{"type":"integer","minimum":1,"maximum":100}
},
"required":["customer_id"]
}
}Why DreamFactory MCP for RAG
- Unified access across SQL Server, MySQL, Postgres with consistent security policies.
- Auto-generated REST with OpenAPI—easy to plug into LangChain, custom agents, or MCP tools.
- RBAC + OAuth/API keys and parameterized queries neutralize injection attempts.
- Zero-credential exposure—LLMs never see DB usernames/passwords.
- Masking & row/field rules to enforce privacy and compliance.
- Audit-grade logging for forensics, dashboards, and compliance evidence.
- Horizontal scalability (containers/serverless) with rate limits and timeouts.
Tip: Standardize response shapes (schemas) so your LLM tools are deterministic, cacheable, and easier to monitor.
Implementation Checklist
- Create
rag-readerrole; deny-by-default; read-only views only. - Generate endpoints for each retrieval task; document via OpenAPI.
- Enforce parameter types, allowlists, and pagination limits.
- Apply field masking (emails, SSNs, tokens); redact at source.
- Set rate limits, timeouts, concurrency caps; add circuit breakers.
- Log identity, role, params, rows returned, region; export to SIEM.
- Adversarial test prompts; verify gateway blocks out-of-policy calls.
- Scale the gateway statelessly; pin data to allowed regions.
FAQs: Secure RAG with SQL Server, MySQL, Postgres
-
Can RAG really improve answer quality?
-
Yes—by injecting live, authoritative data into prompts. Reports indicate substantial accuracy gains (sometimes cited up to ~90%) depending on domain and retrieval quality.
-
Why not let the LLM write the SQL?
-
Direct SQL invites injection, credential exposure, and policy bypass. Gate all access through parameterized, role-scoped APIs.
-
How do I prevent PII exposure?
-
Use field/row-level rules and server-side masking/tokenization so sensitive values never reach the LLM context.
-
What about multi-database environments?
-
Unify access through a single API layer (e.g., DreamFactory MCP) with consistent RBAC, limits, and schemas across SQL Server, MySQL, and Postgres.
-
How do I audit what the AI retrieved?
-
Rely on gateway logs: identity, endpoint, parameters, row counts, region, timestamp, and outcome—sufficient for forensics and compliance.
-
Will this slow us down?
-
No—auto-generated APIs, strict schemas, and reusable security policies accelerate delivery while reducing rework and risk.
Conclusion
RAG unlocks accurate, up-to-date AI—if it’s built on zero-trust rails. By mediating retrieval through a secure, unified API gateway like DreamFactory MCP, you keep credentials hidden, queries parameterized, data minimized, and every call auditable. That’s how enterprises get the best of both worlds: real-time answers and rigorous security.
Kevin McGahey is an accomplished solutions engineer and product lead with expertise in API generation, microservices, and legacy system modernization, as demonstrated by his successful track record of facilitating the modernization of legacy databases for numerous public sector organizations.
























 Blog
Blog