MindsDB has gained attention for its promise to act as a “SQL server for AI”, enabling users to write natural language prompts that convert into executable database queries. While this may appeal to data scientists and AI teams, enterprise CISOs and compliance leaders should proceed with caution.
Recent disclosures have revealed critical security vulnerabilities in MindsDB’s platform that raise serious questions about its suitability for sensitive or regulated environments.
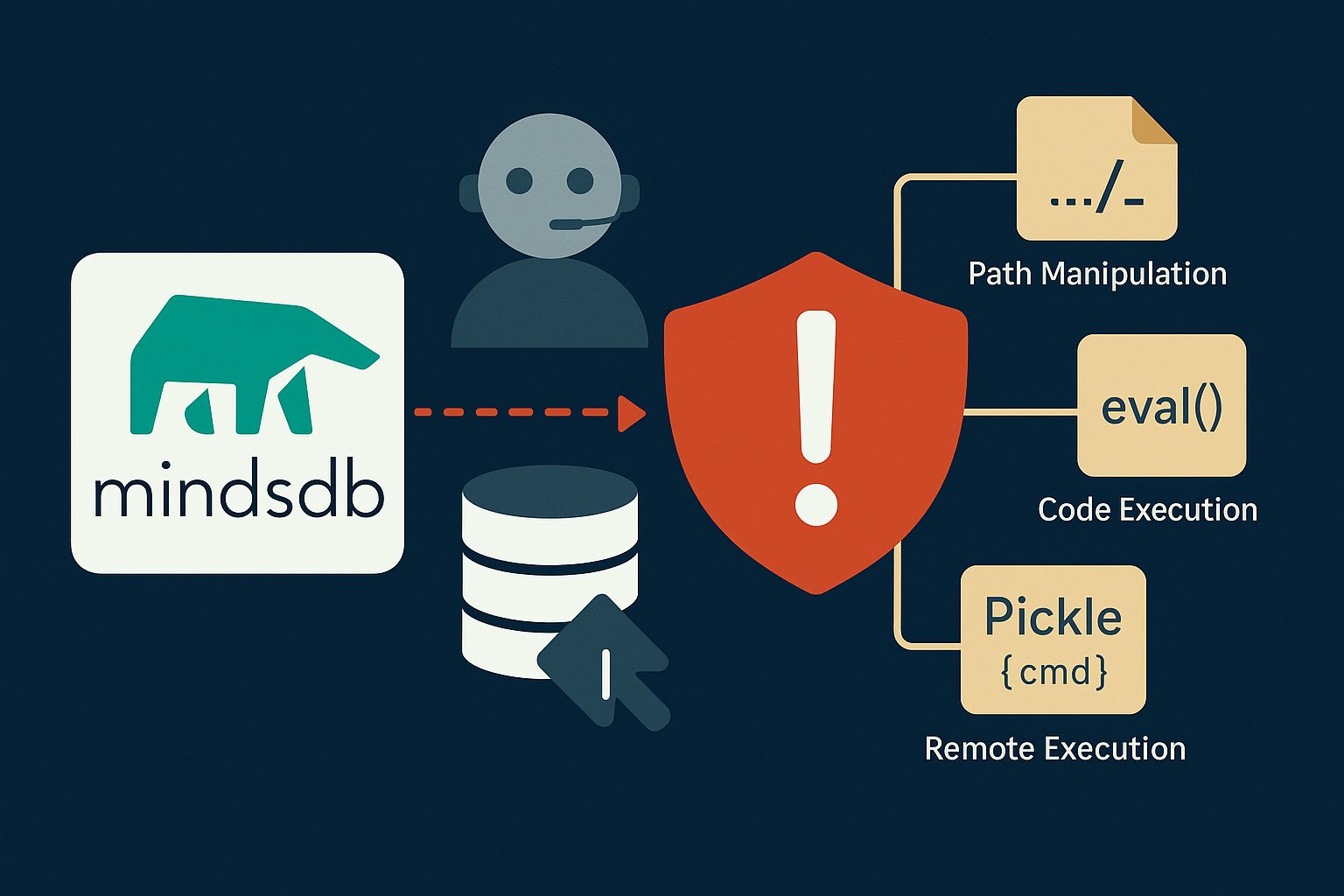
Critical MindsDB Vulnerabilities: A Pattern of Risk
MindsDB’s open nature and complex architecture have made it prone to severe flaws. Examples include:
- Path Manipulation (CVE): A file API endpoint failed to sanitize input, enabling attackers to write or delete arbitrary files on the server.
- Arbitrary Code Execution (CVSS 8.8): Evaluated user inputs with
eval(), allowing attackers to run Python code on the backend. - Remote Execution via Pickle: The “Bring Your Own Model” feature deserialized untrusted Python objects, enabling model files to execute arbitrary commands.
These are not theoretical flaws—they were real, exploitable vulnerabilities that MindsDB patched only after public disclosure. The pattern reveals a codebase with multiple attack surfaces and a high privilege backend that’s difficult to secure holistically.
Architectural Risk: AI with Direct SQL Access
Even aside from bugs, MindsDB’s core design model is high-risk: it empowers AI agents to write SQL queries directly against production databases. This invites several dangers:
- Prompt Injection ➝ SQL Injection: A user may trick the AI into creating a harmful or unauthorized query through cleverly worded prompts.
- No Business Logic Awareness: The LLM might bypass table joins or filters that enforce compliance or internal policies.
- Full SQL Power: AI output can delete, insert, or mutate production data unless carefully sandboxed.
While MindsDB has proposed methods like the “dual LLM pattern” to mitigate these risks, such techniques are experimental, complex, and ultimately still rely on the LLM being correct and secure.
The Safer Alternative: DreamFactory MCP’s Secure AI Gateway Model
Enterprises seeking AI-to-database integration can adopt a fundamentally different approach with DreamFactory’s Model Context Protocol (MCP). Rather than embedding the LLM inside the SQL layer, DreamFactory places a secure, REST API layer between the AI and the database.
Key Benefits of the DreamFactory MCP Architecture
Zero direct SQL access: LLMs query through secure endpoints, not SQL syntax.
- RBAC enforcement: Access is limited by role—e.g., read-only access to safe datasets.
- Parameterized queries: Eliminate SQL injection vectors by sanitizing inputs.
- No eval, no pickle: No deserialization or dynamic code execution anywhere in the loop.
- Audit logging: Every AI interaction is logged for traceability and compliance review.
- Enterprise security stack: OAuth2, API keys, HTTPS transport, rate limiting, and more.
This is a zero-trust model that treats the AI as an untrusted client, subject to the same API rules as any external service. There is no path for AI to construct queries or manipulate the backend—it can only call predefined, validated endpoints.
Preventing Prompt Injection From Becoming a Breach
Even if an attacker uses prompt injection to ask for something sensitive, the DreamFactory API gateway simply denies unauthorized calls. The LLM cannot access anything it hasn’t been explicitly authorized to see. That means:
- No database schema exploration
- No elevation of privileges
- No hidden prompt exploits leading to RCE or exfiltration
Unlike MindsDB, which dynamically builds SQL based on prompts, DreamFactory relies on a static, human-defined query catalog that can be inspected, tested, and monitored. It brings governance and DevSecOps best practices back into the loop.
Conclusion: Choose Secure AI Database Access Over Experimental SQL Agents
While MindsDB offers innovative features, its architecture and security history make it inappropriate for sensitive enterprise use without heavy vetting and additional controls.
DreamFactory’s MCP presents a safer, more mature alternative—turning your database into an API that AI tools can access only through tightly controlled, audit-ready calls.
Don’t give AI your SQL keys—give it a locked door with a keycard. DreamFactory MCP is that door, complete with access logs, guards, and badge scanners built in.
FAQs: MindsDB Security and DreamFactory Alternatives
-
Has MindsDB had real security vulnerabilities?
-
Yes. MindsDB has had critical CVEs, including arbitrary code execution via
eval()and insecure file handling. These flaws allowed attackers to run code or alter server files.
-
What’s the main problem with MindsDB’s architecture?
-
It lets AI models write SQL directly against your production databases, increasing the risk of prompt-to-SQL injection attacks and misaligned query behavior.
-
How is DreamFactory MCP different?
-
DreamFactory MCP exposes database queries as secure, RESTful API endpoints. LLMs can only call these endpoints—not write their own SQL—eliminating most injection and execution risks.
-
Can DreamFactory prevent prompt injection?
-
It can’t stop someone from crafting a misleading prompt—but it ensures any unauthorized request will be rejected by API-level security policies.
-
Does DreamFactory use code execution or Python pickles?
-
No. DreamFactory avoids dangerous patterns like
eval()and untrusted deserialization. All queries are validated and run in a tightly controlled environment.
-
Is this approach compliant with enterprise security standards?
-
Yes. DreamFactory supports role-based access control, OAuth2, encrypted transport, audit logs, and zero-trust design—making it suitable for regulated industries.
-
Can DreamFactory integrate with ChatGPT, Claude, or custom models?
-
Absolutely. LLMs can be configured to call DreamFactory MCP or with RESTful APIs via plugins, function calls, or HTTP interfaces—no SQL access required.
Kevin McGahey is an accomplished solutions engineer and product lead with expertise in API generation, microservices, and legacy system modernization, as demonstrated by his successful track record of facilitating the modernization of legacy databases for numerous public sector organizations.
























 Blog
Blog