When it comes to integrating AI with structured data, traditional Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems often fall short. They rely on indexing and embedding, which can lead to outdated information, security risks, and inefficiencies. Instead, an API-first approach offers a safer, more precise, and real-time solution for accessing structured enterprise data.
Key Takeaways:
- RAG limitations: Prone to stale data, security vulnerabilities, high costs, and inconsistent accuracy (often below 60%).
- API-first benefits: Provides real-time, secure, and accurate data access through pre-approved REST APIs, avoiding risks tied to raw SQL queries.
- Cost-efficiency: Reduces infrastructure costs by up to 70-80% compared to RAG workflows.
- Security: Enforces granular role-based access controls and audit trails, ensuring compliance and protecting sensitive data.
DreamFactory is a secure, self-hosted enterprise data access platform that provides governed API access to any data source, connecting enterprise applications and on-prem LLMs with role-based access and identity passthrough.
What is RAG? The Complete Tutorial - From Scratch to Deployed API on Production | LangChain & Ollama
What is RAG for Structured Data?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an AI framework that ties large language models (LLMs) to external, enterprise-specific knowledge sources. This setup allows the AI to generate more precise outputs without requiring extensive fine-tuning. Essentially, RAG enables AI systems to pull in external data - tailored to a business's needs - during processing.
When applied to structured data, RAG systems tap into databases and spreadsheets to retrieve specific details, like account statuses or payment records. This approach ensures AI responses are grounded in factual, business-relevant information. As McKinsey & Company puts it:
"RAG allows LLMs to access and reference information outside the LLMs own training data, such as an organization's specific knowledge base, before generating a response - and, crucially, with citations included".
Here's how the process works. The ingestion phase converts structured data into a format that’s easy to search and index, mapping database schemas and indexing records. During the retrieval phase, algorithms comb through this index to find relevant details, often using SQL queries or API calls to pull specific data points like "Customer X paid on Jan 15". Finally, in the generation phase, the LLM uses these retrieved facts to create a natural language response, ensuring the output reflects up-to-date, accurate information.
The RAG Process for Structured Data
The workflow kicks off when a user submits a query to the AI. A lightweight LLM or intent detection tool identifies the user’s needs and extracts key parameters like customer IDs or dates. Unlike traditional RAG, which relies on vector similarity searches, structured RAG uses deterministic queries. This means it formulates precise queries to fetch exact values from relational databases, CSV files, or in-memory caches like Redis.
The retrieved data is typically returned in structured formats like JSON. From there, it’s converted into human-readable sentences or "canonical rows" and fed into the LLM's context window. This deterministic method minimizes the risk of errors like "semantic drift" or numeric inaccuracies - issues that could have serious consequences in fields like aerospace or healthcare. As Alejandro Reyes Amaro, an AI Integration Specialist, points out:
"In compliance-oriented environments (chemical piping, aerospace part matching, medical dosages, …) almost correct is absolutely wrong".
To maintain security, modern implementations often place an API gateway between the AI and the database. This setup ensures the LLM doesn’t execute raw SQL directly, protecting against SQL injection attacks and safeguarding sensitive credentials.
Where RAG is Used in AI Applications
RAG for structured data is used across various enterprise scenarios. In customer service, chatbots access real-time account data and company policies to deliver personalized support without requiring agents to dig through multiple systems. For business analytics, drafting assistants pull data from spreadsheets and databases to prepopulate reports, helping finance teams close books faster or enabling quick inventory checks. In knowledge management systems, RAG synthesizes information from an organization’s intranet, offering actionable insights to employees.
This framework is especially useful in environments where internal APIs dominate - 58% of APIs developers work with are for internal purposes, providing secure access to enterprise data. By grounding responses in live, authoritative data, RAG can improve LLM accuracy by up to 90% in business intelligence and support contexts.
While the benefits are clear, implementing RAG for structured data comes with its own set of challenges. Let’s explore these obstacles and why some organizations are exploring alternative solutions.
Problems with RAG for Structured Data
While RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) shows potential, applying it to structured data comes with a host of technical and operational challenges. Its reliance on offline indexing and embedding introduces issues with accuracy, security, and overall efficiency.
Main Technical Challenges
Security risks: Allowing raw SQL queries within RAG systems opens the door to vulnerabilities like SQL injection, credential exposure, and violations of PII (Personally Identifiable Information) controls. Kevin McGahey, Solutions Engineer and Product Lead at DreamFactory, highlights the dangers:
"Direct SQL invites injection, credential exposure, and policy bypass. Gate all access through parameterized, role-scoped APIs."
Stale data is another significant issue. Traditional RAG workflows rely on offline indexing, where data is chunked and embedded. For enterprises with frequently changing data - such as inventory levels or customer account statuses - this approach creates a bottleneck. Re-indexing becomes resource-intensive, and outdated data may lead to incorrect insights. Niko Berry, Product Manager at Contentful, notes:
"Highly dynamic data, like stock levels or weather updates, forces constant re-indexing, increasing cost and reducing efficiency."
Performance degradation adds to the complexity. Allowing large language models (LLMs) to write freeform SQL can result in inefficient queries that strain production databases. As data volumes grow, retrieval latency worsens, requiring advanced indexing or sharding techniques.
Accuracy problems remain a persistent challenge. Even with optimizations, traditional RAG pipelines often fail to retrieve the correct data chunks consistently, with accuracy rates frequently falling below 60%. The reliance on semantic similarity can lead to "semantic drift", where the system retrieves related but contextually incorrect data, undermining the reliability of business intelligence applications.
Permissions complexity: Managing access permissions is another sticking point. Structured data often comes with intricate access control lists (ACLs) inherited from source systems. RAG requires replicating these permissions in vector databases, which increases the risk of compliance failures and data leaks. Brian Yam, Head of Marketing at Paragon, explains:
"By ingesting structured data into vector stores, you're essentially trying to reinvent database functionality that already exists - and doing it less effectively."
These challenges highlight the disconnect between RAG's design and the demands of enterprises working with structured data.
RAG vs. Required Data Access Capabilities
When comparing RAG's performance to enterprise needs, the gaps become evident:
|
Enterprise Requirement |
RAG Performance |
Technical Impact |
|---|---|---|
|
Real-Time Data Access |
Delayed (depends on indexing cycles) |
AI systems may deliver outdated metrics; synchronization lags lead to "stale data" |
|
Security & Compliance |
Broad, document-level access |
Requires duplicating permissions, increasing the risk of leaks and PII exposure |
|
Query Accuracy |
Semantic similarity (approximate) |
Prone to hallucinations; retrieval accuracy often below 60% |
|
Scalability |
Limited by vector DB performance |
Retrieval latency grows with data size; aggressive sharding becomes necessary |
|
Operational Cost |
High (syncing, chunking, re-indexing) |
Re-indexing dynamic data is resource-intensive and expensive |
|
Database Performance |
Risk of performance regressions |
AI-generated SQL can overwhelm production databases with inefficient queries |
These shortcomings demonstrate why enterprises dealing with dynamic structured data are seeking alternatives that offer deterministic access, built-in security, and real-time updates - without the burdens of vector indexing.
The API-First Approach for Structured Data
Tackling issues like outdated data and security vulnerabilities, the API-first approach skips traditional indexing methods. Instead, it uses secure REST APIs as the main interface, delivering structured JSON or CSV data directly to AI systems or applications. This method avoids exposing databases, ensuring a safer and more reliable data exchange.
This strategy provides real-time, predictable access to structured data, eliminating the need for offline indexing, vector databases, or constant re-embedding whenever data updates. Applications and AI agents can access live data through endpoints like GET /api/customers?filter=active&limit=100, consistently receiving accurate, up-to-date responses. By removing the delays inherent in retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) workflows, this approach integrates effortlessly into enterprise systems.
How API-First Data Access Works
The API-first model relies on an API gateway that acts as a bridge between applications and data sources. This gateway connects to systems like MySQL, Oracle, or SQL Server, dynamically creating REST endpoints for each resource. For example, calling GET /api/sales/Q3/summary provides aggregated and structured data.
The gateway handles several critical tasks: routing requests, caching responses, authenticating users, and transforming data. It enforces schema validation, rate limiting, and role-based access controls before any data leaves its source. This setup eliminates direct database connections, reducing the risk of breaches and ensuring consistent data formatting. Unlike RAG, which involves multiple steps like ingestion and retrieval, the API-first approach delivers live data with sub-second latency.
This abstraction layer also supports multi-tenancy and works across different environments. Whether data is stored on-premises in SQL Server or in a cloud-hosted PostgreSQL instance, the gateway offers a unified interface. Enterprises can modernize gradually, wrapping older databases in REST APIs without undertaking costly migrations.
Why Enterprises Choose API-First
Now, let’s explore why this approach is gaining traction among enterprises.
Instant access to live data is a game-changer. API endpoints provide real-time data, making them perfect for dashboards, AI systems, and analytics that demand up-to-the-minute accuracy. For instance, a query for "Q3 sales vs. trends" yields precise figures, unlike outdated approximations from older embedding techniques.
Built-in security is another major advantage. APIs leverage existing database roles - like those from Active Directory - without requiring custom coding. Access controls are applied to each request, ensuring AI systems and applications operate within pre-defined security guidelines. Additionally, audit logs document every data access instance, providing the transparency needed for compliance.
Consistent and accurate query results are critical for business intelligence and financial reporting. APIs ensure that identical queries always return the same results, something large language models (LLMs) often struggle with. While LLMs can produce errors or "hallucinate" about 15–20% of the time, API-driven approaches achieve up to 97% accuracy, thanks to their reliance on verified structured data. One example showed that a RAG API reduced escalations by 90%, slashing costs from over $2,000 to just $499 per month for 10,000 queries.
Lower infrastructure costs make this approach even more appealing. By replacing complex ETL pipelines and vector databases with a single API layer, companies can cut infrastructure expenses by 70–80%. This eliminates the need for preprocessing, chunking, and storage costs associated with RAG workflows. The "wrap, don’t rip" strategy also allows enterprises to integrate AI with their existing systems immediately, while upgrading their infrastructure at their own pace.
How DreamFactory Delivers API-First Data Access
DreamFactory is an open-source REST API gateway designed to automatically generate secure and documented APIs for over 30 database and service connectors. These include popular systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, SQL Server, Oracle, AWS S3, and SFTP, among others. By addressing the challenges of direct database access, DreamFactory acts as a "data plane" or abstraction layer, enabling seamless integration between legacy and modern databases. As Terence Bennett, CEO of DreamFactory, puts it:
"DreamFactory becomes your on‑prem 'data layer' that connects your existing data to any AI, analytics, or front‑end system".
DreamFactory's self-hosted model gives enterprises full control over their deployment. It can be run on bare metal, virtual machines, or containers (using Docker or Kubernetes) across Linux and Windows environments [7,37]. This setup ensures that data remains securely on-premises, whether in air-gapped systems, private clouds, edge computing setups, or hybrid environments. Because the platform is stateless and portable, scaling is effortless. Beyond securing data, DreamFactory simplifies integration with AI and analytics workflows.
Core DreamFactory Features
DreamFactory's REST API abstraction layer transforms how businesses access structured data. Instead of connecting directly to databases, applications and AI systems interact with governed REST endpoints that the platform automatically generates for each connected resource. These endpoints handle routing, caching, authentication, and data transformation.
One standout feature is identity passthrough. DreamFactory integrates with existing authentication systems like Okta, OAuth, LDAP, and Active Directory, ensuring that real user identities are preserved in every API request.
The platform supports over 30 connectors, covering SQL databases, NoSQL systems, cloud storage, and external APIs. Developers can also use Event Scripts to trigger custom business logic - written in JavaScript, PHP, or Python - before or after an API call. Additionally, the System API provides tools for programmatic management of users, services, and roles, supporting DevOps and automation workflows.
AI Integration and Security
DreamFactory takes AI integration a step further by incorporating advanced security measures. To address the security gaps often found in retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) systems, DreamFactory employs robust controls. One key feature is its Model Context Protocol (MCP) server, which standardizes AI access. This protocol allows AI agents to interact with live, governed data without exposing sensitive credentials. For example, AI systems can query vetted REST endpoints (e.g., GET /api/customers?filter=active&limit=100) and receive structured JSON responses based on real-time data.
Security is further strengthened through Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), offering granular permissions down to the field level. Sensitive data, like Social Security numbers or financial information, can be anonymized using data masking and tokenization before reaching AI agents or clients. Each API interaction generates a detailed audit trail, complete with timestamps and source tracking. As Bennett explains:
"Every AI action is bounded by your policies and leaves a trail. Visibility without another shadow system".
To guard against SQL injection attacks, DreamFactory uses parameterized queries, input validation, and query whitelisting. It also employs AI-driven traffic analysis to detect anomalies, such as unusual request spikes or repeated access failures, adding another layer of protection. With a 4.7/5 rating on G2, DreamFactory has demonstrated its effectiveness across industries like finance, manufacturing, the public sector, and healthcare.
API-First vs. RAG: Direct Comparison
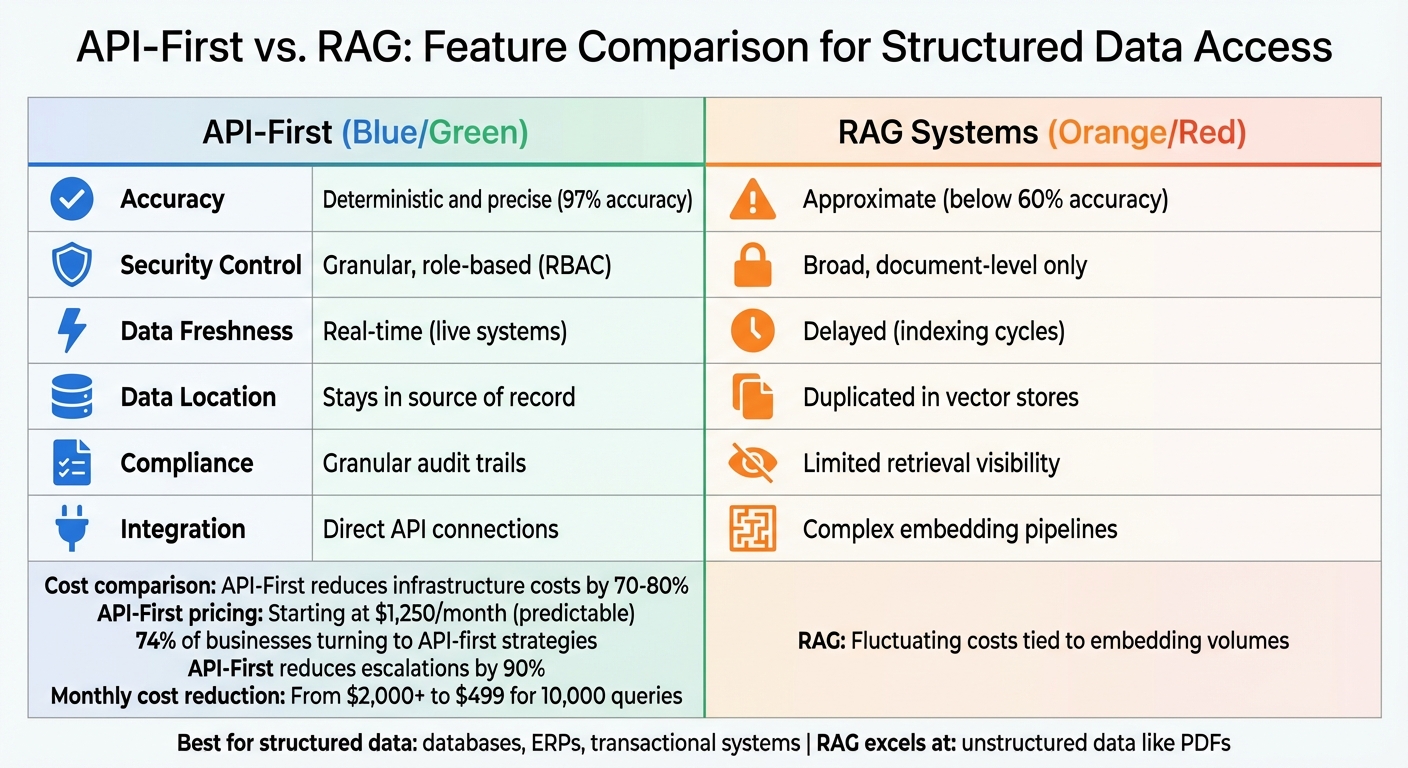
API-First vs RAG Systems: Feature Comparison for Structured Data Access
Feature Comparison Table
Here’s how API-First and RAG systems measure up across six key areas:
|
Aspect |
API-First (Agent-Based) |
RAG Systems |
|---|---|---|
|
Accuracy |
Deterministic and precise |
Approximate |
|
Security Control |
Granular, role-based (RBAC) |
Broad, document-level only |
|
Data Freshness |
Real-time (live systems) |
Delayed (indexing cycles) |
|
Data Location |
Stays in source of record |
Duplicated in vector stores |
|
Compliance |
Granular audit trails |
Limited retrieval visibility |
|
Integration |
Direct API connections |
Complex embedding pipelines |
The API-first model is a natural fit for structured systems like databases, ERPs, and transactional platforms where real-time precision is non-negotiable. On the other hand, RAG systems excel when handling unstructured data, such as PDFs, but often fall short in terms of accuracy and governance - essential features for enterprise-grade databases.
Cost-wise, the two models differ sharply. API-first solutions, like DreamFactory, offer predictable pricing starting at $1,250/month, aligning well with enterprise needs. RAG systems, however, come with fluctuating costs tied to embedding volumes and vector database usage. Notably, 74% of businesses are turning to API-first strategies to enhance scalability and streamline integration efforts.
These distinctions highlight why DreamFactory is specifically designed to address the challenges of RAG systems.
How DreamFactory Solves RAG Limitations
DreamFactory builds on the strengths of API-first architectures to tackle the shortcomings of RAG systems in three critical ways:
- Eliminating Query Risks
DreamFactory removes the risks tied to direct SQL generation by offering pre-approved, parameterized REST endpoints. This approach avoids the common pitfalls of prompt injection and performance bottlenecks that arise when AI models generate database queries. - Real-Time Data Access
Unlike RAG systems, which rely on duplicating data into vector stores, DreamFactory connects directly to live databases. Its REST API abstraction layer supports MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, MongoDB, and over 30 other systems. This ensures AI agents have access to up-to-date information without creating unnecessary shadow data copies. - Enhanced Security and Compliance
DreamFactory delivers granular security measures that go beyond what RAG systems can offer. Server-side scripting safeguards sensitive data - like Social Security numbers or email addresses - before it reaches the AI. Additionally, every API interaction is logged with detailed timestamps, providing an audit trail that meets stringent compliance standards.
DreamFactory’s Model Context Protocol (MCP) ensures AI agents request data within predefined policy boundaries, making the platform model-agnostic. This flexibility allows enterprises to switch between AI models without overhauling their data architecture. Combined with a strong 4.7/5 rating on G2, these features solidify API-first as the preferred choice for secure, structured data access.
Implementing API-First with DreamFactory
Setup and Configuration Steps
To get started with DreamFactory, you can deploy it using Docker, Kubernetes (via Helm charts), or traditional installation methods. Once deployed, head over to the Services tab to create a new service. Select your data source - whether it's MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, SQL Server, or MongoDB - and input the required connection details, such as the Host, Port, Database Name, Username, and Password. After saving, DreamFactory will automatically generate a REST API, complete with full CRUD operations and OpenAPI documentation.
For securing your API, create a Role to define specific permissions. This can include restrictions at the table level or limiting access to certain HTTP verbs. Then, create an App and link it to the role, which will generate a unique X-DreamFactory-Api-Key for authenticating requests.
Next, deploy the MCP server using the command-line tool. Configure the .env file with your database credentials and register the base URL and API key with compatible AI clients like Claude Desktop or OpenAI Agent Builder. These AI systems can now securely interact with your data through REST endpoints, eliminating the need for raw SQL queries.
"MCP servers create a secure bridge between AI language models and legacy databases, exposing database tools that AI clients can call with proper permissions." - DreamFactory
For additional security, create a dedicated database user with read-only (SELECT) permissions to prevent data modification or potential SQL injection attacks. To further optimize performance, enable Data Retrieval Caching in the service configuration, which helps reduce the load on older systems. If you're working under compliance frameworks like GDPR or HIPAA, you can configure field-level masking to redact sensitive data - such as Social Security or credit card numbers - ensuring that this information is never exposed to AI systems.
Converting Legacy Systems to API-First
Once your API is securely set up, you can start modernizing your legacy systems. DreamFactory makes this process straightforward by converting outdated protocols into REST APIs. For example, you can import a WSDL file in the Services > SOAP section, and DreamFactory will automatically create REST endpoints that handle both authentication and data transformation. This eliminates the need for fragile, script-based integrations.
For systems located behind firewalls, DreamFactory supports SSH tunneling, allowing secure access without exposing your database to outside threats. You can also add custom business logic using server-side scripting languages like PHP, Python, or Node.js. This is particularly useful for validating inputs or transforming data formats from legacy systems.
To streamline governance and scaling, you can use DreamFactory's System APIs to manage users, services, and roles programmatically across multiple environments. This ensures consistent management and security as your system evolves.
Deployment and Security Configuration
Deployment Options
DreamFactory offers multiple deployment methods, including on-premises, air-gapped, hybrid, and private cloud setups. These options ensure your structured data stays within controlled infrastructure, catering to various security and compliance needs.
On-premises deployments install the entire API platform directly on your servers, giving you full control over data access. This method is ideal for organizations requiring complete data locality to meet strict compliance standards like GDPR or HIPAA.
Air-gapped deployments are designed for environments with no Internet connectivity. Using offline installation packages and manual license activation, these setups eliminate any internet exposure. DreamFactory can still connect to legacy databases like Oracle or SQL Server without relying on external networks, making it a strong choice for high-security environments.
Hybrid deployments combine the best of both worlds by routing data queries through on-premises APIs while utilizing cloud services for AI inference. Secure channels like VPN or AWS PrivateLink ensure data remains protected. DreamFactory's API gateway acts as a proxy, keeping raw data within your infrastructure. One manufacturing company reported reducing costs by 80% compared to full cloud solutions, all while retaining full control over sensitive data like proprietary bill-of-materials.
Private cloud deployments allow DreamFactory to run on dedicated cloud instances. This setup delivers the scalability of the cloud while maintaining control over sensitive data, making it a flexible option for businesses with specific security requirements.
Once you choose a deployment method, the next step is to implement strong security and monitoring protocols.
Security and Monitoring Setup
After deployment, securing your APIs and monitoring their performance are critical steps.
Start by configuring authentication mechanisms like JWT or OAuth 2.0, paired with IP whitelisting and CORS policies to tightly control access. For additional protection, integrate a web application firewall (WAF) to shield against threats like SQL injection and DDoS attacks. Studies show that this setup can block 99% of common attacks.
Rate limiting is another essential feature to maintain system stability. You can set limits based on users, roles, or endpoints, typically ranging from 100 to 500 requests per minute per IP. This is particularly useful for enterprises processing over 1 million API calls daily, as it prevents system overload and reduces costs from excessive retries caused by AI errors, which can otherwise increase expenses by up to 40%.
For real-time insights, DreamFactory provides a /metrics endpoint compatible with Prometheus, which collects data every 15 seconds. These metrics are visualized in Grafana dashboards, offering a clear view of latency, error rates, and throughput. With a Docker Compose setup, you can deploy this monitoring stack in under 30 minutes, enabling faster issue resolution - up to 95% quicker than troubleshooting retrieval logs manually. Additionally, enable audit logging to track every API call, ensuring compliance and complete traceability of AI interactions with your data.
Conclusion
When dealing with structured data, an API-first architecture offers clear advantages over RAG: consistent outputs, precise numerical handling, and strong security measures. While RAG is effective for retrieving unstructured text, it adds unnecessary complications and risks when used with databases, data warehouses, or enterprise systems that already operate within well-defined schemas.
The benefits of API-first approaches are clear: they can deliver up to 97% accuracy, lower escalation rates by 90%, and reduce monthly costs from over $2,000 to about $499 for 10,000 queries.
DreamFactory exemplifies these advantages with its API-first implementation. It generates governed REST APIs instantly, enabling secure, real-time data integration for both legacy and modern systems. The platform ensures security through features like identity passthrough, role-based access controls, and detailed audit trails. By eliminating direct database access, it also removes the risk of prompt-to-SQL injection.
Rather than relying on probabilistic methods like RAG, secure your data with APIs. With DreamFactory's on-premises, air-gapped, and hybrid deployment options, enterprises can modernize legacy systems and accelerate AI initiatives without compromising security, compliance, or control. This approach ensures your data remains secure while AI retrieves accurate, governed answers - delivering the best of both worlds. It’s a smart and secure way to align data modernization with enterprise needs.
FAQs
What security advantages does an API-first approach offer for accessing structured data?
An API-first approach offers strong security benefits for accessing structured data by providing better control, governance, and protection for sensitive information. With governed REST APIs, organizations can enforce precise, role-based access, making sure that only authorized users and systems can interact with the data. This reduces exposure and embeds security measures directly into the API layer, ensuring consistent application of authentication, authorization, and auditing processes.
This method also strengthens data governance by tightly managing access requests and supporting compliance with regulations. Unlike approaches that involve duplicating or migrating data - which can create security risks - an API-first strategy enables live, secure access without generating vulnerable copies. By incorporating AI-driven automation into the API layer, businesses can further tighten security, simplify policy enforcement, and minimize potential attack points, all while maintaining data integrity and scalability.
How does an API-first approach help lower infrastructure costs compared to RAG systems?
An API-first approach can dramatically cut infrastructure costs by offering direct and secure access to enterprise data. Unlike methods that require duplicating data into resource-intensive systems like vector databases, this strategy connects to existing data sources through governed REST APIs. This eliminates the need for computationally heavy processes like high-dimensional embeddings and constant re-indexing.
One key benefit is the use of deterministic AI queries, which make data retrieval predictable and efficient. This eliminates the complexity and expense of similarity-based searches. Additionally, API-first solutions minimize the need for large, specialized data stores or redundant data copies, helping organizations save on storage, migration, and operational costs. With live, on-demand access to data, this approach not only keeps costs in check but also ensures security and governance are upheld.
Why is real-time access to structured data important for enterprises, and how does an API-first approach deliver it?
Real-time access to structured data is crucial for businesses aiming to make quick, informed decisions, optimize their operations, and improve customer interactions. Having access to the most current data allows organizations to adapt swiftly to changes, cut down on delays, and ensure that critical tasks are always supported by accurate information. This is especially critical in fields like finance, healthcare, and manufacturing, where even small delays can lead to major issues.
An API-first approach makes real-time data access seamless by creating secure, governed REST APIs that directly connect to existing data sources, such as SQL databases, legacy systems, or file repositories. This approach removes the need to duplicate or migrate data, which helps avoid delays and prevents reliance on outdated information. These instantly generated APIs provide live, dependable data access, ensuring that AI tools, applications, and teams can operate smoothly without interruptions. On top of that, this strategy supports scalability while allowing businesses to maintain full control over their data, no matter which cloud environment they use.
Konnor Kurilla is a technical engineer with experience supporting API-driven workflows, troubleshooting backend systems, and developing documentation that empowers users to understand and utilize their technology. Blending customer-focused thinking with hands-on technical skills, he helps bridge the gap between product complexity and user clarity.
























 Blog
Blog


